Hotline
+86-136 8495 9862
Email:cennia@szmizhi.com
Add::104,Building 27,Third Industrial Zone, Longxi Community,Longgang District,Shenzhen,China.
Coil Forming & Handling Equipment
Surface Treatment Equipment
Solutions
Application
About Us

Welcome to MIZHI
For consultation/feedback, please call the service hotline: +86-136 8495 9862 Email:cennia@szmizhi.com

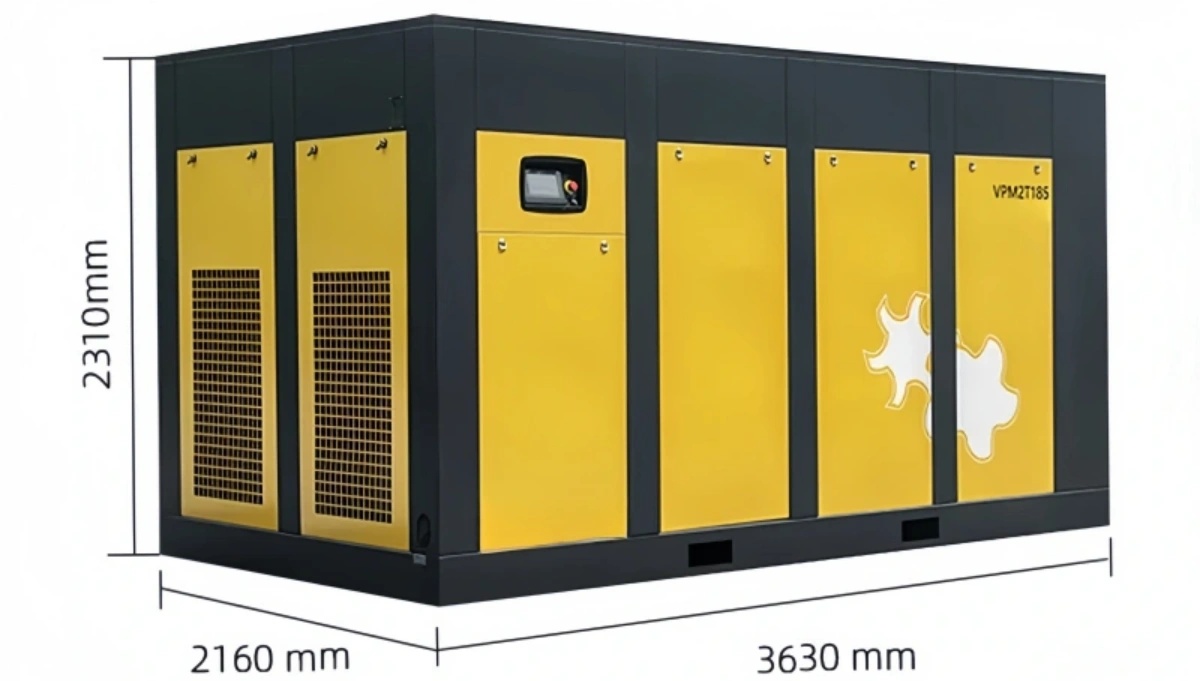
An air compressor is a versatile and essential piece of equipment used across various industries to convert power (usually from an electric motor or a gas/diesel engine) into potential energy stored in compressed air. This compressed air can then be utilized to power a wide range of tools and equipment.

Here’s a comprehensive introduction to air compressors:
Basic Principle
An air compressor works by drawing in atmospheric air, compressing it to a higher pressure, and then storing this compressed air in a storage tank. The compressed air can be released and used as needed to power tools, inflate objects, or drive pneumatic systems.
Key Components
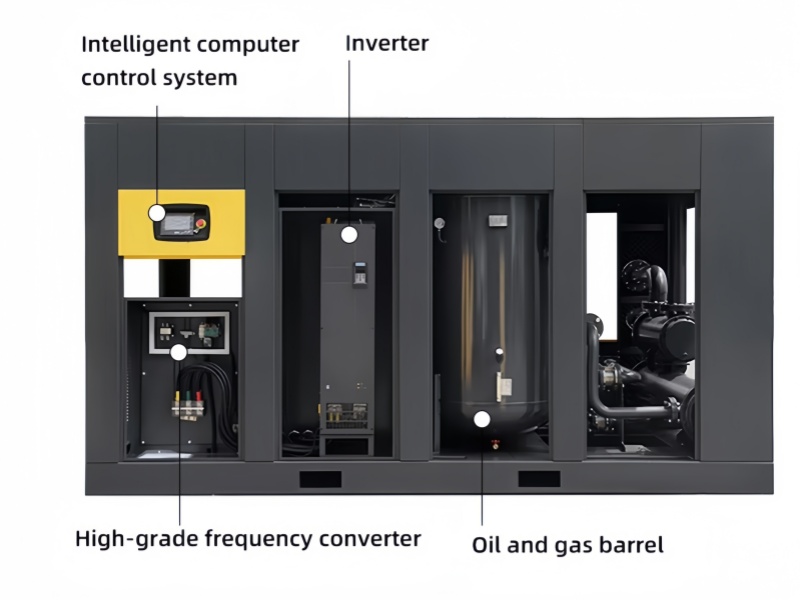
1.Compressor Pump: This is the heart of the machine, responsible for compressing the air. It can be of various types, such as reciprocating (piston), rotary screw, or centrifugal.
2.Storage Tank: The compressed air is stored here until it is needed. The tank helps regulate the pressure and provides a steady supply of air.
3.Motor/Engine: This component powers the compressor pump. It can be electric, gasoline, or diesel-powered, depending on the application.
4.Valves and Regulators: These control the flow and pressure of the compressed air, ensuring it is delivered at the desired pressure and volume.
5.Air Intake Filter: Prevents dust and debris from entering the compressor, protecting the internal components.
6.Pressure Relief Valve: Ensures safety by releasing excess pressure if the system exceeds its rated capacity.

Types of Air Compressors
1.Reciprocating (Piston) Compressors:
(1) Single-Stage: Compresses air in one stroke, suitable for lower pressure applications.
(2) Two-Stage: Compresses air in two stages, achieving higher pressures and efficiencies.

(3) Advantages: High efficiency, suitable for intermittent use.
(4) Applications: Construction, automotive repair, and small workshops.
2.Rotary Screw Compressors:
(1) Principle: Uses two intermeshing screws to compress air continuously.
(2) Advantages: Continuous operation, high efficiency, and low maintenance.
(3) Applications: Industrial manufacturing, large-scale operations, and continuous air supply needs.
3.Centrifugal Compressors:
(1) Principle: Uses rotating impellers to compress air through centrifugal force.
(2) Advantages: High capacity, suitable for very high-pressure applications.
(3) Applications: Power plants, large industrial facilities, and HVAC systems.
Applications
Air compressors are used in a wide range of industries and applications:
1.Construction: Powering tools like nail guns, drills, and air hammers.
2.Automotive: Running air tools in repair shops, inflating tires, and painting.
3.Manufacturing: Driving pneumatic tools, operating assembly lines, and powering robotic systems.
4.Medical: Supplying compressed air for medical equipment and breathing apparatus.
5.Food and Beverage: Used in packaging, bottling, and cleaning processes.
6.Oil and Gas: Powering tools and equipment in drilling and refining operations.
Benefits
1.Versatility: Can power a wide range of tools and equipment.
2.Efficiency: Converts electrical or mechanical energy into usable compressed air.
3.Safety: Reduces the need for electrical tools in hazardous environments.
4.Durability: Many compressors are designed for long-term, heavy-duty use.
5.Portability: Smaller units can be easily moved around job sites.
Maintenance Tips
1.Regular Inspection: Check for leaks, wear, and damage.
2.Filter Replacement: Replace air intake filters regularly to prevent dust buildup.
3.Oil Changes: Ensure the compressor oil is changed as recommended by the manufacturer.
4.Drain the Tank: Regularly drain the storage tank to prevent water accumulation.
5.Check Valves and Regulators: Ensure they are functioning correctly to maintain proper pressure.
In summary, air compressors are indispensable in modern industry and construction, providing a reliable source of power for a wide range of applications. Their versatility, efficiency, and durability make them a valuable asset in any workplace.